About Microservices
What are Microservices:
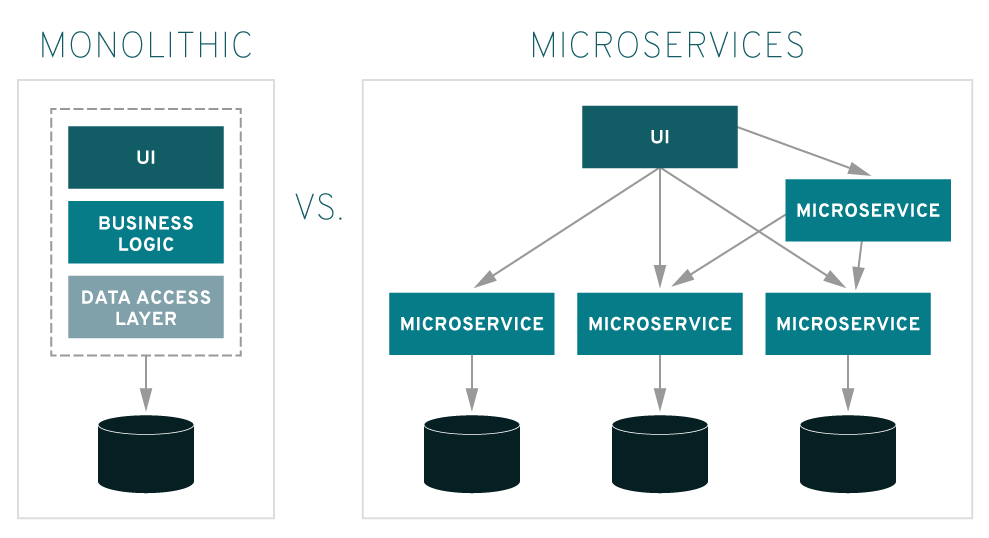
Microservices - also known as the microservice architecture - is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are
- Often times large monolithic applications that are broken into small services.
- Highly maintainable and testable
- Loosely coupled
- Independently deployable
- Organized around business capabilities
- Owned by a small team
The microservice architecture enables the rapid, frequent and reliable delivery of large, complex applications. It also enables an organization to evolve its technology stack.
Benefits of Microservices:
Act Independently : Microservices are applications that are separated into a collection of small, independently deployable services. Because microservices are designed to act independently, they are naturally consistent with agile principles that promote end-to-end team ownership.
Simplified Deployment: Each microservice is built and aligned around a feature to reduce the complexity of the application change-management process. Because each service is individually changed, tested, and deployed without affecting other services, deployment is accelerated.
Improved Application Quality: Because of the "divide-and-conquer" approach of microservices, both functional and performance testing are easier with microservices than they are with monolithic applications. Microservices architecture lends itself to test-driven development, as components can be tested in isolation and combined with a full or virtualized set of microservices. This approach results in overall improvement in application quality.
Easier to Scale: Teams can more efficiently scale applications by scaling individual services according to their criticality to the overall app, throughput, memory, and CPU load.
Rules for Building Applications with Microservices:
When you develop microservices for an application, keep these rules in mind:
One job: Each microservice must be optimized for a single function. Each service is smaller and simpler to write, maintain, and manage. Robert Martin calls this principle the "single responsibility principle."
Separate processes: Communication between microservices must be conducted through REST API and message brokers. All communication from service to service must be through the service API or must use an explicit communication pattern, such as the Claim Check Pattern from Hohpe.
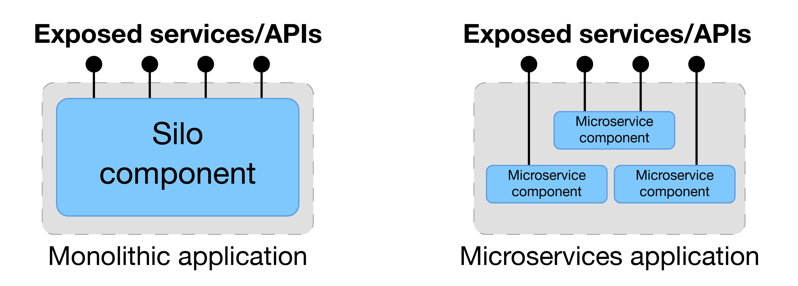
Execution scope: Although microservices can expose themselves through APIs, the focus is not on interfaces, but on the running components. The granularity of a microservices application is highlighted in this figure:
CI/CD: Each microservice can be continuously integrated (CI) and continuously delivered (CD). When you build a large application that is composed of many services, you soon realize that different services evolve at different rates. If each service has a unique continuous integration or continuous delivery pipeline, the service can proceed at its own pace. In the monolithic approach, different aspects of the system are all released at the speed of the slowest moving part of the system.
Resiliency: You can apply high availability and clustering decisions to each microservice. When you build large systems, another realization that you have is that when it comes to clustering, one size does not fit all. The monolithic approach of scaling all the services in the monolith at the same level can lead to the overuse or underuse of services. Even worse, when shared resources are monopolized, services might be neglected. In a large system, you can deploy services that do not need to scale to a minimum number of servers to conserve resources. Other services require scaling up to large numbers.
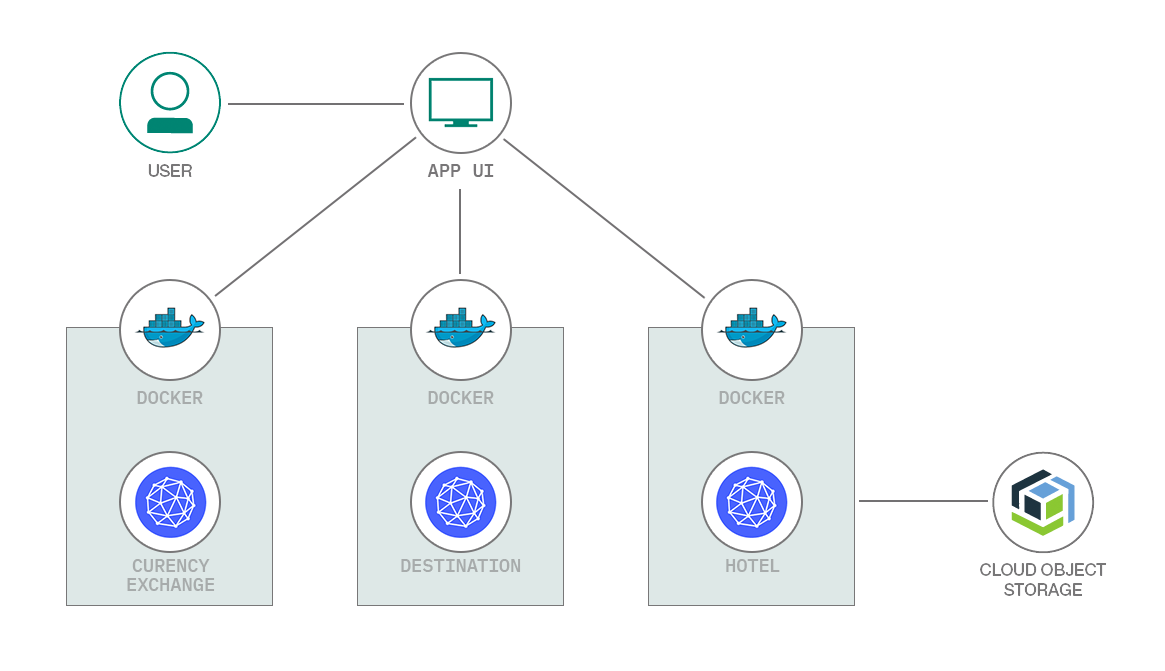
Architecture:
Bee Travels is a travel booking application that is composed of several mircoservices. Each mircoservice can be run independently, or together to form the full service. Bee Travels can be used to search and book hotels, flights and car rentals for various destinations across the world.
Note: All data is fake and only to be used for demonstration purposes.
Bee Travels is comprised of the following microservices:
- UI Frontend
- UI Backend
- Destination
- Hotel
- Car Rental
- Flight
- Currency Exchange
- Checkout
- Payment
The following is a basic architecture diagram for the containerized v1 version of Bee Travels.